
Radar | Oct 16,2021
Aug 3 , 2024
By Mushe Semu
The recent macroeconomic overhaul in a country experiencing economic development and diplomatic pressure has ignited a firestorm of controversy. Advocates argue that the policy could usher in growth and development, while critics caution against possible serious pitfalls. Given the high stakes, it is crucial to unpack the potential implications for Ethiopia's economy and its citizens.
The government lauds the proposed policy's merits, yet critics note a lack of thorough consideration of potential downsides. They warn that any policy enacted by executive order could ricochet, fueling chronic economic instability, a predicament that requires a careful evaluation of near-term effects.
The International Monetary Fund (IMF), in its research published in "Financial Development," warns that while floating exchange rates may address overvaluation risks, they do not necessarily guarantee low inflation, diminished volatility, or enhanced trade integration, compared with fixed exchange-rate regimes.
Comparative analysis reveals a mixed bag. Context is king, as each country’s unique economic milieu has influenced the outcomes.
Countries like Spain, Greece, Iceland, and Poland have had inconsistent results with floating exchange rates. China's strategic approach of managing an exchange rate to boost exports is evident in the notion that prudent management, not full-blown liberalisation, can produce higher economic results.
A case in point is Singapore, a country with a positive trade balance, that has chosen a managed floating policy, facilitating regulated fluctuation within stipulated limits.
In contrast, Ethiopia’s considerable trade deficit demands a more cautious approach.
Despite the potential benefit of exchange rate liberalisation, Ethiopia’s complexities demand careful consideration of associated risks. A completely liberalised exchange rate could trigger uncertain economic outcomes, with considerable risks of inflation bursts, currency value instability, and a hit to overall economic productivity.
For a country like Ethiopia, struggling with high demand and supply shortages, a system based on a free-floating exchange rate could invite erratic currency fluctuations. This unpredictability could make it harder to forecast economic trajectory, thereby pouring cold water on investor confidence.
Another looming concern should be Ethiopia's depleted foreign currency reserves. Leaning heavily on market forces to determine exchange rates could further destabilise prices and pose formidable economic challenges.
Devaluation of the Birr could drive up the cost of imports, including essential services and goods. This could fan the flames of inflation, impacting the cost of living and potentially fueling social unrest. Ethiopia's economic productivity is already under duress due to ongoing conflicts that impact exports and overall economic stability. An unrestrained floating exchange rate could potentially exacerbate these issues rather than remedy them.
Policies should strike a balance between short-term pressures and long-term stability, keeping the average Ethiopian economic welfare front and centre. Comprehensive strategies encompassing managed exchange rates and targeted economic reforms could be the key to unlocking sustainable development in Ethiopia.
PUBLISHED ON
Aug 03,2024 [ VOL
25 , NO
1266]


Radar | Oct 16,2021

Fortune News | Jan 23,2021

Fortune News | Dec 25,2021

Fortune News | Oct 16,2021

Fortune News | Oct 23,2021

Commentaries | Jul 10,2021
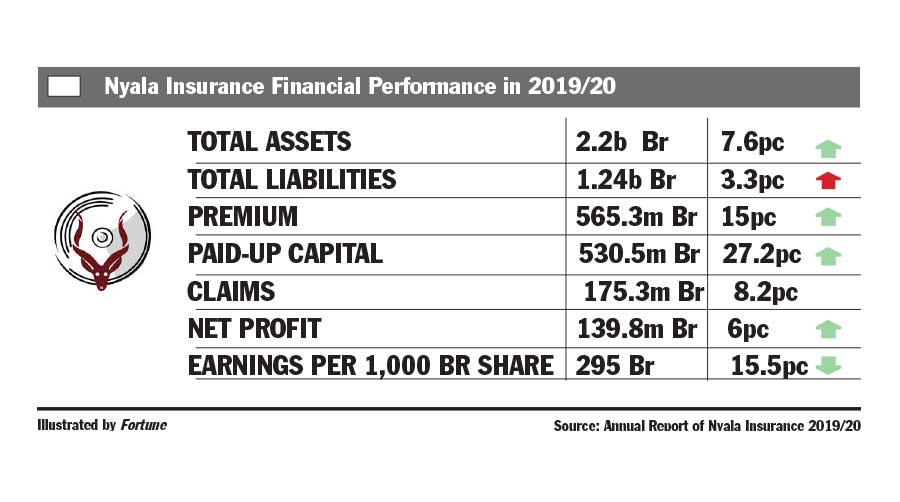
Fortune News | Feb 27,2021

Radar | May 23,2020
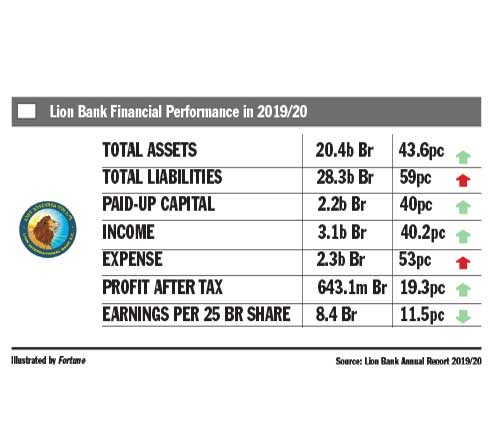
Fortune News | Mar 13,2021

Editorial | Feb 05,2022

My Opinion | 131970 Views | Aug 14,2021

My Opinion | 128359 Views | Aug 21,2021

My Opinion | 126297 Views | Sep 10,2021

My Opinion | 123912 Views | Aug 07,2021

Dec 22 , 2024 . By TIZITA SHEWAFERAW
Charged with transforming colossal state-owned enterprises into modern and competitiv...

Aug 18 , 2024 . By AKSAH ITALO
Although predictable Yonas Zerihun's job in the ride-hailing service is not immune to...

Jul 28 , 2024 . By TIZITA SHEWAFERAW
Unhabitual, perhaps too many, Samuel Gebreyohannes, 38, used to occasionally enjoy a couple of beers at breakfast. However, he recently swit...

Jul 13 , 2024 . By AKSAH ITALO
Investors who rely on tractors, trucks, and field vehicles for commuting, transporting commodities, and f...

Jul 5 , 2025
Six years ago, Ethiopia was the darling of international liberal commentators. A year...

Jun 28 , 2025
Meseret Damtie, the assertive auditor general, has never been shy about naming names...
Jun 21 , 2025
A well-worn adage says, “Budget is not destiny, but it is direction.” Examining t...

Jun 14 , 2025
Yet again, the Horn of Africa is bracing for trouble. A region already frayed by wars...
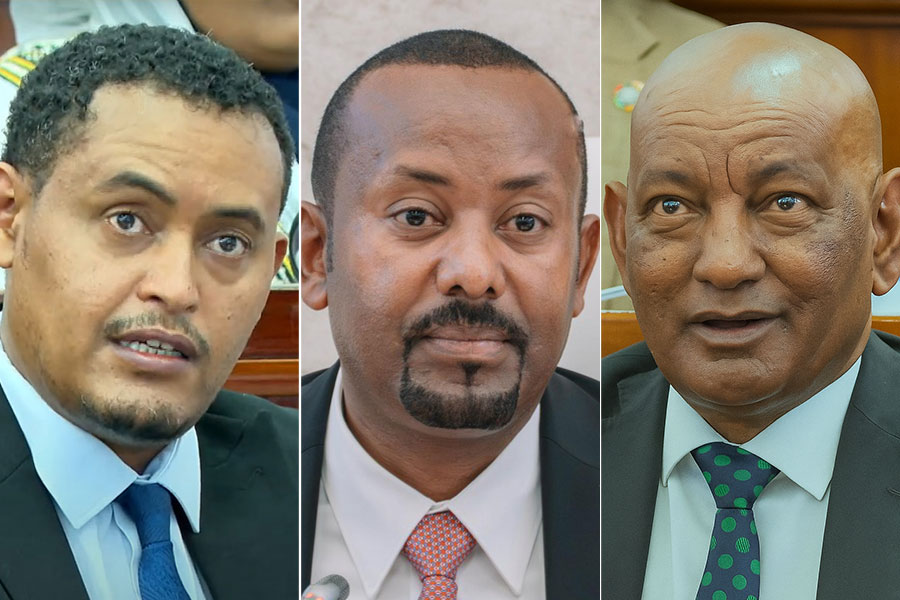

Jul 6 , 2025 . By BEZAWIT HULUAGER
The federal legislature gave Prime Minister Abiy Ahmed (PhD) what he wanted: a 1.9 tr...

Jul 6 , 2025 . By YITBAREK GETACHEW
In a city rising skyward at breakneck speed, a reckoning has arrived. Authorities in...

Jul 6 , 2025 . By NAHOM AYELE
A landmark directive from the Ministry of Finance signals a paradigm shift in the cou...

Jul 6 , 2025 . By NAHOM AYELE
Awash Bank has announced plans to establish a dedicated investment banking subsidiary...