Editorial | Jun 24,2023
Jan 12 , 2019
By Belay Abera
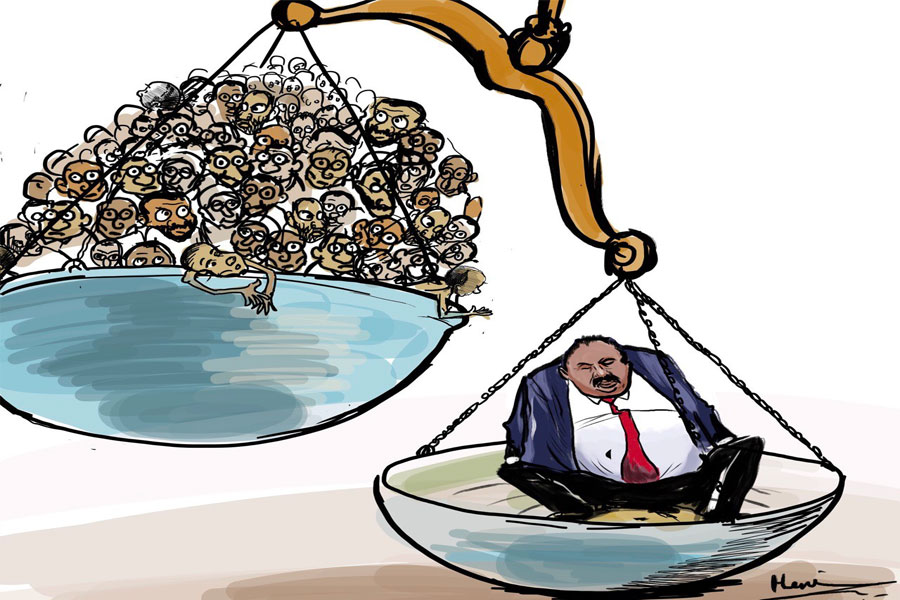
Nothing comes free in this world, not even aid. There are implied preconditions behind every largesse by one country to another. But international aid persists, either by governmental or non-profit organisations, considering developing countries lack of resources, especially in times of crisis such as natural or human-made disasters.
Depending on the purpose, it usually comes in the form of goods, such as food or medicines, or just direct payments to victims or institutions. It is one of the fruits of the globalised world, where developed countries have come to believe such support to a nation anywhere in the world has its benefits either for one’s global agenda or to make the world a more stable place.
International aid may not be perfect but, in many cases, it has been shown to be of extreme importance. It is hard to discount the support countries such as Ethiopia get from the various agencies of the United Nations or the United States Agency for International Development.
African countries are mostly the biggest recipients of aid, mainly on poverty reduction, development and healthcare. Many international agencies provide economic and humanitarian assistance in Africa, especially in Sub-Saharan Africa. It is not hard to guess why: the economic circumstance of the region gives a glaring justification. In Ethiopia’s case, the government plans to get 19 billion Br from external assistance in this year alone.
Incredibly enough, it has been going on for over the past half century. Since African countries began to win their independence from European powers. Unfortunately, there is little to show for the hundreds of billions of dollars in aid that has been poured into African countries ever since the 1960s.
It is a result of the institutional and leadership incompetence in African countries to ensure that aid reaches the target population. Without the necessary checks and balances and transparency, it is not such a mystery why much of the aid that pours into the continent can rarely be accounted for.
A stark example of this was when the UN’s World Food Programme found that food aid meant for victims of famine in 2011 Somalia was being stolen. It was after 3.2 million people were said to be in need of food assistance after drought and civil war combined to create famine affected zones. The fact that food meant for those in dire need, including children, was being diverted and sold in marketplaces should show the scale of the inability of not just aid organizations but also governments to ensure that aid is efficiently distributed where it will have the most impact.
The Somalia example is one of many incidents that happen to international aid in Africa. And it is just a drop in the bucket of aggregate failures of international aid programs to reach their targets.
Historically, the movement of foreign aid has been very difficult to follow. It is not simply clear how the aid money or food aid is spent and whether the aid is reaching the target communities.
The best means of addressing this problem for countries such as Ethiopia is strengthening institutions by improving transparency and checks and balances in government.
Digital registration systems could be vital in mapping out how and where aid flows and improving the public’s knowledge of international aid finances and resources. Such systems can register donor’s names, type of donation, the timing of donation, beneficiaries’ statuses, concerned governmental organisations and system of donation. The system should also be supported by a small survey of beneficiaries randomly selected from all gender and age groups to assess whether the aid has really reached the beneficiaries.
This requires political will, but the payoff would be large. The proper administration of every bit of assistance can save from the need to want for more when a crisis arises.
PUBLISHED ON
Jan 12,2019 [ VOL
19 , NO
976]


Editorial | Jun 24,2023

Radar | Sep 14,2019

Fortune News | Nov 09,2019

Fortune News | Dec 04,2022

Radar | Jan 04,2020

Editorial | Jan 30,2021

Radar | Mar 20,2021

Fortune News | Feb 29,2020

Fortune News | Jun 07,2020

Radar | Mar 06,2021

Photo Gallery | 174762 Views | May 06,2019

Photo Gallery | 164984 Views | Apr 26,2019

Photo Gallery | 155227 Views | Oct 06,2021

My Opinion | 136724 Views | Aug 14,2021
Editorial | Oct 11,2025

Dec 22 , 2024 . By TIZITA SHEWAFERAW
Charged with transforming colossal state-owned enterprises into modern and competitiv...

Aug 18 , 2024 . By AKSAH ITALO
Although predictable Yonas Zerihun's job in the ride-hailing service is not immune to...

Jul 28 , 2024 . By TIZITA SHEWAFERAW
Unhabitual, perhaps too many, Samuel Gebreyohannes, 38, used to occasionally enjoy a couple of beers at breakfast. However, he recently swit...

Jul 13 , 2024 . By AKSAH ITALO
Investors who rely on tractors, trucks, and field vehicles for commuting, transporting commodities, and f...

Oct 11 , 2025
Ladislas Farago, a roving Associated Press (AP) correspondent, arrived in Ethiopia in...

Oct 4 , 2025
Eyob Tekalegn (PhD) had been in the Governor's chair for only weeks when, on Septembe...
Sep 27 , 2025
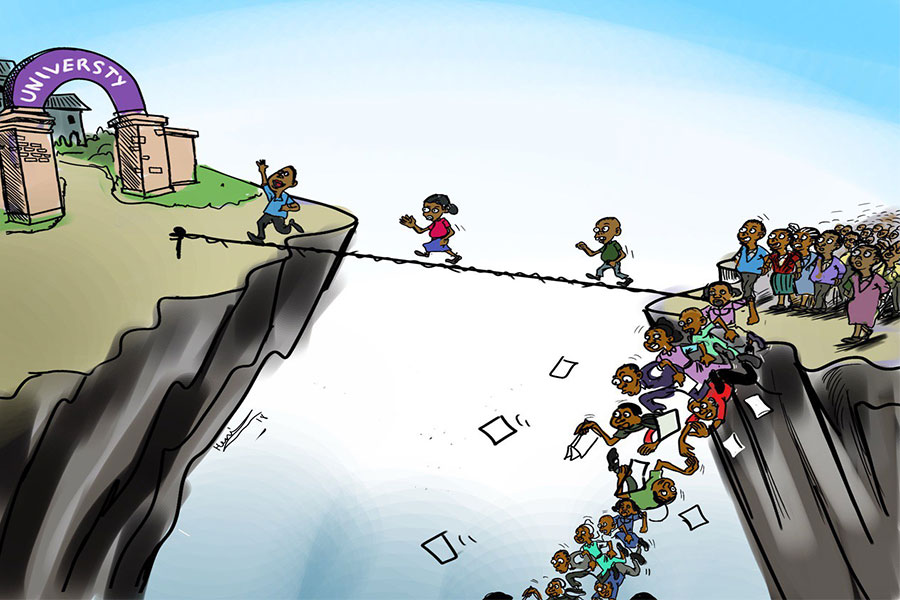
Four years into an experiment with “shock therapy” in education, the national moo...
Sep 20 , 2025
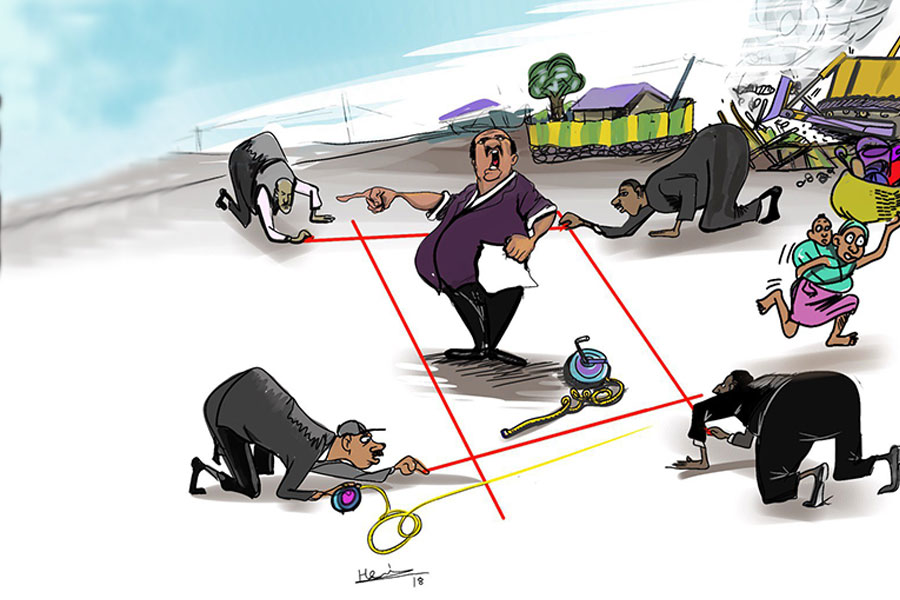
Getachew Reda's return to the national stage was always going to stir attention. Once...

Oct 12 , 2025
Tomato prices in Addis Abeba have surged to unprecedented levels, with retail stands charging between 85 Br and 140 Br a kilo, nearly triple...

Oct 12 , 2025 . By BEZAWIT HULUAGER
A sweeping change in the vehicle licensing system has tilted the scales in favour of electric vehicle (EV...

A simmering dispute between the legal profession and the federal government is nearing a breaking point,...

Oct 12 , 2025 . By NAHOM AYELE
A violent storm that ripped through the flower belt of Bishoftu (Debreziet), 45Km east of the capital, in...