
Fortune News | Aug 11,2024
Oct 20 , 2024
The banking sector is poised to take on a greater role in the larger economic playing field. By leveraging technological advancements, for instance, and by integrating sophisticated treasury management systems, they can improve cash flow and liquidity management, gain real-time visibility into financial positions, and enhance decision-making processes. In these trying times, the ability of banks to adapt and move forward will be the true test of their relevance and resilience, argues this commentary, whose author's identity we withheld upon request.
Ethiopia's transition to a floating exchange rate is a moment of profound opportunity for banks to modernise, innovate, and set the stage for a more dynamic and competitive financial environment.
However, the coming years will test bankers' resolve, creativity, and leadership. Those who rise to the challenge, embracing the uncertainties of the floating exchange rate system with a strategic and proactive approach, will no doubt go beyond securing their position in the market. They will contribute to the broader goal of economic stability and growth.
The shift to a floating exchange rate regime fundamentally transforms operational dynamics. It introduces new uncertainty in foreign and local currency liquidity, demanding the refinement of liquidity management practices. This includes bolstering foreign currency reserves, developing contingency funding plans, mobilising local currency resources, and ensuring optimal alignment between asset and liability maturities.
While potential long-term benefits include enhanced market efficiency and economic adaptability, the immediate consequences could be daunting. Some of these pressures are heightened exchange rate volatility, escalating inflationary pressures, and acute liquidity constraints.
Bankers should consider adopting a strategic approach rooted in strengthening risk management, rethinking product offerings, engaging the market proactively, enhancing export competitiveness, and boosting remittances.
Strengthening risk management is an understatement. Bankers should fortify their capacities to manage foreign exchange, credit, and liquidity risks to safeguard financial stability.
Credit risk management should be enhanced, as currency depreciation increases import costs, potentially compromising the creditworthiness of borrowers reliant on foreign inputs. Banks should improve their credit risk assessment frameworks to account for exchange rate fluctuations and their impact on borrowers' ability to service debt.
Foreign exchange risk management requires developing and deploying sophisticated hedging instruments such as forward contracts, options, and swaps. Although these tools are not yet fully available, collaboration with international financial institutions could facilitate access and prepare banks for future market developments. Bankers should reassess their foreign currency exposure limits and integrate dynamic risk assessment models that reflect new levels of volatility.
Bankers should implement real-time pricing models for foreign exchange transactions, allowing clients to execute trades at rates that reflect the prevailing market. Expanded trade finance solutions can include currency-linked loans, import financing with built-in hedging options, and structured trade finance products designed to protect clients from exchange rate risks. Investment products for foreign currency, such as foreign currency–denominated accounts and fixed deposits offering competitive returns, can attract and retain foreign currency deposits and investments.
Banks will assume the heavy burden of educating their clients on the implications of the floating exchange rate system and the tools available to manage associated risks. Tailored workshops, webinars, and personalised advisory sessions will help.
Competitiveness in the export sector will define the game to mobilise foreign exchange. Banks can support exporters by developing export financing products, including pre-and post-shipment financing. Supporting small and medium enterprises, often the bedrock of export growth, with tailored financial products and services, will be crucial. Partnering with government agencies and international financial institutions to offer export guarantees and insurance can protect exporters against political and commercial risks.
Banks should also develop remittance-linked products, such as foreign currency accounts and investment opportunities, offering competitive returns for remittance recipients. Streamlining remittance channels by reducing fees, offering attractive forex rates, and improving the speed and convenience of transfers can encourage using formal banking channels. Proactively engaging with the diaspora communities builds trust and encourages remittance flows.
Leveraging technological advancements, such as integrating sophisticated treasury management systems, is critical in managing the challenges posed by the floating exchange rate system. These systems help to improve cash flow and liquidity management, provide real-time visibility into financial positions, and improve decision-making processes.
PUBLISHED ON
Oct 20,2024 [ VOL
25 , NO
1277]

Fortune News | Aug 11,2024
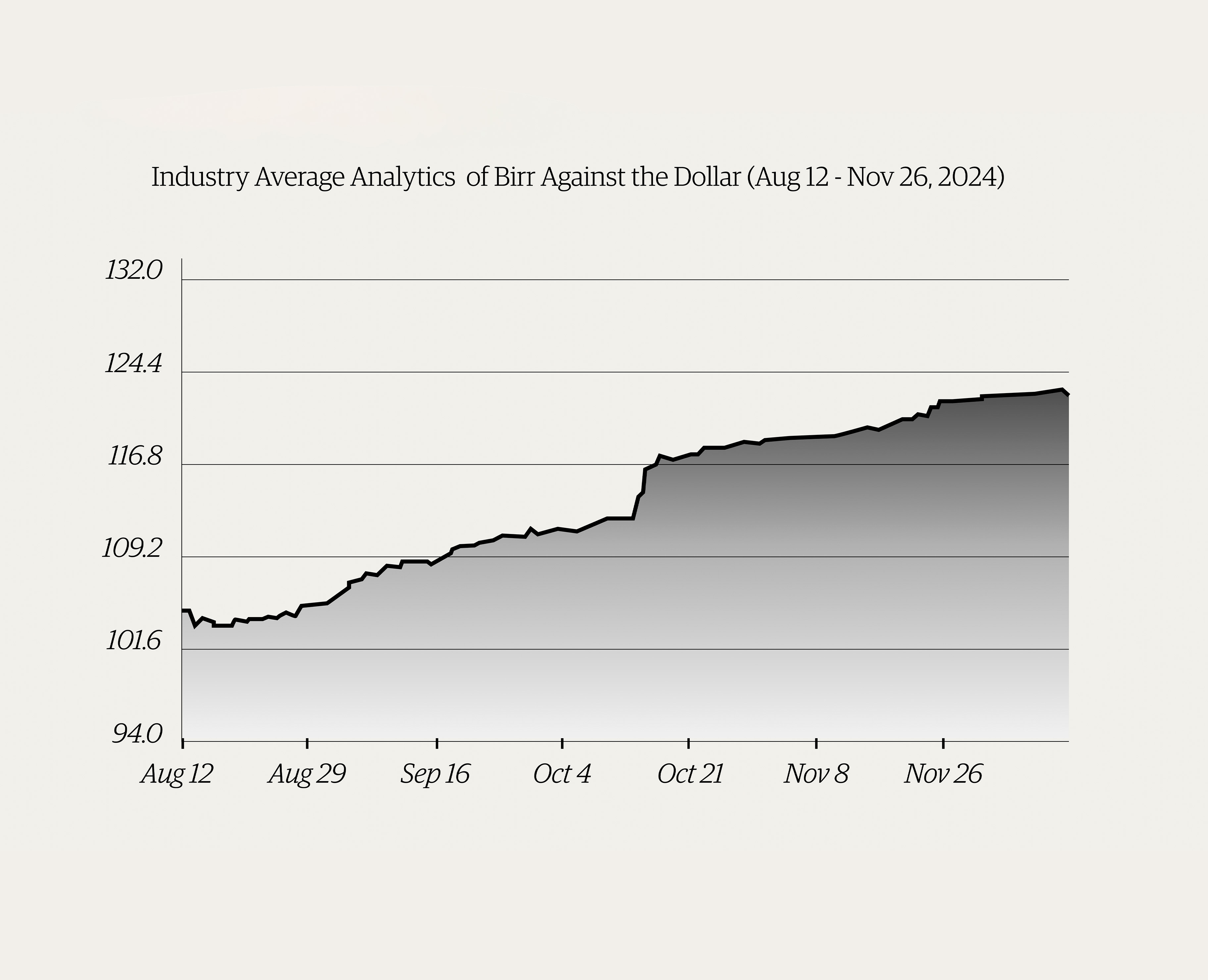
Money Market Watch | Dec 15,2024

Agenda | Apr 13,2024

Fortune News | Mar 07,2020

Agenda | Sep 11,2020

Fortune News | Mar 09,2024

Fortune News | Jul 06,2025

Agenda | Apr 15,2023

Commentaries | Sep 01,2024

Commentaries | Dec 25,2018

Photo Gallery | 174751 Views | May 06,2019

Photo Gallery | 164971 Views | Apr 26,2019

Photo Gallery | 155214 Views | Oct 06,2021

My Opinion | 136724 Views | Aug 14,2021
Editorial | Oct 11,2025

Dec 22 , 2024 . By TIZITA SHEWAFERAW
Charged with transforming colossal state-owned enterprises into modern and competitiv...

Aug 18 , 2024 . By AKSAH ITALO
Although predictable Yonas Zerihun's job in the ride-hailing service is not immune to...

Jul 28 , 2024 . By TIZITA SHEWAFERAW
Unhabitual, perhaps too many, Samuel Gebreyohannes, 38, used to occasionally enjoy a couple of beers at breakfast. However, he recently swit...

Jul 13 , 2024 . By AKSAH ITALO
Investors who rely on tractors, trucks, and field vehicles for commuting, transporting commodities, and f...

Oct 11 , 2025
Ladislas Farago, a roving Associated Press (AP) correspondent, arrived in Ethiopia in...

Oct 4 , 2025
Eyob Tekalegn (PhD) had been in the Governor's chair for only weeks when, on Septembe...
Sep 27 , 2025
Four years into an experiment with “shock therapy” in education, the national moo...
Sep 20 , 2025
Getachew Reda's return to the national stage was always going to stir attention. Once...

Oct 12 , 2025
Tomato prices in Addis Abeba have surged to unprecedented levels, with retail stands charging between 85 Br and 140 Br a kilo, nearly triple...

Oct 12 , 2025 . By BEZAWIT HULUAGER
A sweeping change in the vehicle licensing system has tilted the scales in favour of electric vehicle (EV...

A simmering dispute between the legal profession and the federal government is nearing a breaking point,...

Oct 12 , 2025 . By NAHOM AYELE
A violent storm that ripped through the flower belt of Bishoftu (Debreziet), 45Km east of the capital, in...