
Radar | May 25,2024
Aug 27 , 2022
By Christian Tesfaye
No one really can predict the future. The advances in collecting, collating and analysing large amounts of data are impressive. But they have not taken humanity as near to clairvoyance as was hoped.
Take, for instance, the predictions on the aftermath of the invasion of Ukraine by Russia. The coverage all around was about doom and gloom. A potential nuclear strike being provoked was discussed; prices for a barrel of oil hitting 200 dollars; and famines in many places being caused by skyrocketing food prices.
The war was and continues to be ugly, but the worst did not happen. In fact, oil prices are below pre-war levels, as well as global food prices. Geopolitical tensions continue to simmer and food prices are still high by historical standards. But many dire predictions did not pan out. Consider even how every pundit agreed that Russia would take over Kyiv, the Ukrainian capital, within a few days until it became all too clear that it had no hope of doing as such.
Or consider the repeated grim assessments of China’s economy. Capital outflows shortly after the war in Europe were supposed to crash the economy. Before that, it was the default by the major real estate developer, Evergrande, which was supposed to be the Lehman-Brothers-collapse moment for China. The country is obviously in a property market crisis, but it is not nearly the calamity it was suggested to be at the outset; not to mention, Evergrande is still standing.
The cherry on the cake was predictions about COVID-19 cases in Africa at the outset of the pandemic. The most morbid reports came from Italy first, with hospitals barely coping with the influx. If Europe struggles so much to arrest the disease, how would Africa, which has the poorest health infrastructure in the world, ever cope? Biblical levels of suffering, it was said, were in store for African countries.
The pandemic was no joke, and its economic and public health effects continue to be felt. But it was nothing like it was predicted to be by the analysts. It has been a struggle to explain why, but the pandemic has been much more manageable in Africa than in the rest of the world, especially considering there have not been full lockdowns.
Why are we so bad at predicting events?
One reasonable explanation is bias. Most of the time, we are expressing what may be based on how we see the world and not necessarily on how it is in reality. We make assumptions that fit our worldviews and ideologies. Even experts have a hard time maintaining an entirely objective stance. The philosophical debate on whether research could be fully objective should be settled by now. It is most likely not the case.
It is also true that most of us are pessimistic. Look at most estimates about events over the past few years, and it is clear that they portray most occurrences as being worse than is otherwise the case. We see a Hitler, an economic calamity or major war in every nook and cranny. It is not that things are not bad. It is just that they are not as bad as advertised – not as grim as the activists and TV channels that want to keep us glued to our screens claim.
It probably has to do with our biological evolution. Our brains are better hardwired to record and respond to potentially alarming developments than they are to good news, because the former could be existential. It is our fight-or-flight psychology at work. The problem is that it was not designed for a world where so much bad news is easily accessible.
Our obsession with data and its analysis makes sense. It is an effort to take subjectivity out of predictions. But this has proven harder than anticipated. We need much more data to map events accurately, including human’s psychological tendency to overreact.
PUBLISHED ON
Aug 27,2022 [ VOL
23 , NO
1165]


Radar | May 25,2024
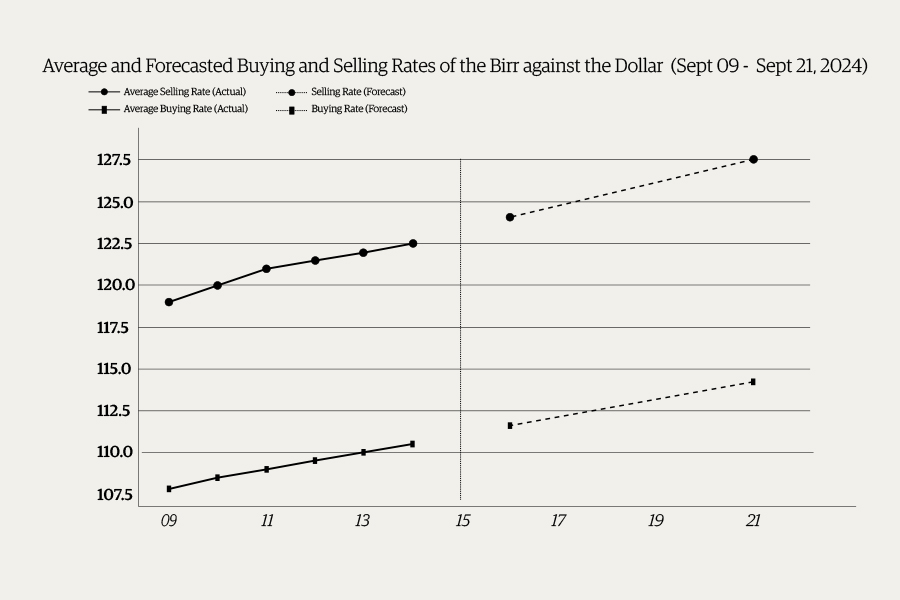
Money Market Watch | Sep 14,2024

Sunday with Eden | Apr 13,2019

Sunday with Eden | Feb 13,2021
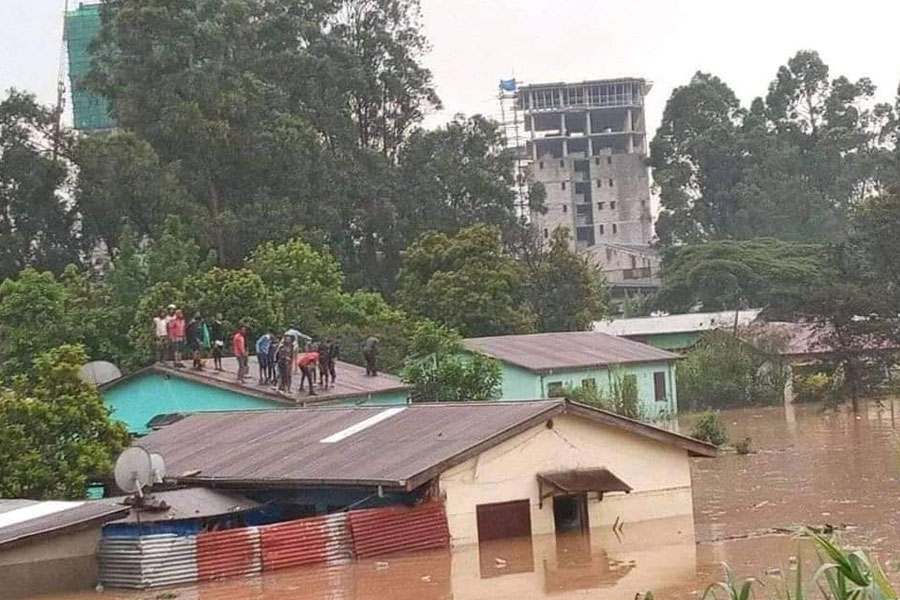

News Analysis | Aug 21,2021

Radar | Nov 21,2018

Covid-19 | Apr 25,2020

Radar | Sep 18,2022

Radar | Oct 31,2020

View From Arada | Aug 17,2019

Photo Gallery | 174667 Views | May 06,2019

Photo Gallery | 164890 Views | Apr 26,2019

Photo Gallery | 155110 Views | Oct 06,2021

My Opinion | 136704 Views | Aug 14,2021
Editorial | Oct 11,2025

Dec 22 , 2024 . By TIZITA SHEWAFERAW
Charged with transforming colossal state-owned enterprises into modern and competitiv...

Aug 18 , 2024 . By AKSAH ITALO
Although predictable Yonas Zerihun's job in the ride-hailing service is not immune to...

Jul 28 , 2024 . By TIZITA SHEWAFERAW
Unhabitual, perhaps too many, Samuel Gebreyohannes, 38, used to occasionally enjoy a couple of beers at breakfast. However, he recently swit...

Jul 13 , 2024 . By AKSAH ITALO
Investors who rely on tractors, trucks, and field vehicles for commuting, transporting commodities, and f...

Oct 11 , 2025
Ladislas Farago, a roving Associated Press (AP) correspondent, arrived in Ethiopia in...

Oct 4 , 2025
Eyob Tekalegn (PhD) had been in the Governor's chair for only weeks when, on Septembe...
Sep 27 , 2025
Four years into an experiment with “shock therapy” in education, the national moo...
Sep 20 , 2025
Getachew Reda's return to the national stage was always going to stir attention. Once...

Oct 12 , 2025
Tomato prices in Addis Abeba have surged to unprecedented levels, with retail stands charging between 85 Br and 140 Br a kilo, nearly triple...

Oct 12 , 2025 . By BEZAWIT HULUAGER
A sweeping change in the vehicle licensing system has tilted the scales in favour of electric vehicle (EV...

A simmering dispute between the legal profession and the federal government is nearing a breaking point,...

Oct 12 , 2025 . By NAHOM AYELE
A violent storm that ripped through the flower belt of Bishoftu (Debreziet), 45Km east of the capital, in...