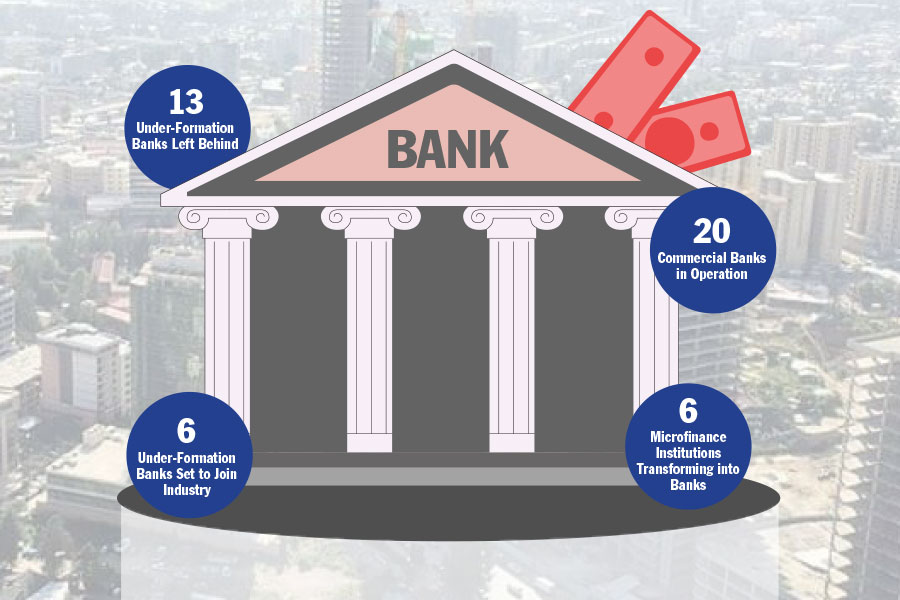
Fortune News | Oct 16,2021
May 23 , 2021
By Akim Mohamed Daouda , Uche Orji and Mamadou Mbaye
Although African sovereign wealth funds have already shown their effectiveness, their potential remains largely untapped. By mobilising and leveraging national savings, these funds not only can increase governments’ capacity to finance public policies but also help to attract much-needed foreign capital, write Akim Mohamed Daouda, Uche Orji and Mamadou Mbaye, CEOs of Gabonese Strategic Investment Fund, Nigeria Sovereign Investment Authority and Djibouti Sovereign Fund, respectively.
On May 18, African heads of state, European leaders, and representatives of international institutions will gather in Paris for a summit on financing African economies. As heads of African sovereign wealth funds (SWFs), we strongly believe that mobilising national resources – and using them to attract additional foreign capital – is the only way to ensure our economies’ financial independence.
The COVID-19 pandemic has exposed the lingering vulnerabilities of African economies. They remain too sensitive to exchange-rate risk, unable to finance themselves, and too dependent on donors. In addition, adverse risk perceptions mean that most international investors and asset managers still have only a marginal presence on the continent.
But Africa urgently needs to attract international capital. After the continent’s pandemic-induced recession in 2020, the African Development Bank expects real GDP to grow by only 3.4pc this year. This projected recovery will not generate the resources we need to meet our development needs.
Financing Africa’s development will require governments to think of new ways to secure international investments without increasing their debt – and using the continent’s SWFs is one of the most credible options. As in many other countries around the world, these state-controlled institutions manage national surpluses with the aim of building wealth and providing a sound financial foundation on which governments can formulate ambitious development or diversification policies.
Over the last decade, 15 African countries – including Morocco, Nigeria, Gabon, Rwanda, Senegal, and, more recently, Djibouti – have established SWFs. According to a recent report by the International Forum of Sovereign Wealth Funds, these funds currently manage a total of 24 dollars billion in assets. While this amount is not comparable to the size of other SWFs internationally, it is nonetheless significant in the context of African economies.
Our SWFs are proof that African countries also can be financially innovative. Countries such as Senegal, Rwanda, and Djibouti have understood that such funds are not only for commodity-rich economies. At the same time, oil producers such as Gabon and Nigeria are using their SWFs to diversify resource allocation and adapt to the evolving economic context. In each case, these funds base their strategies on rigorous management of national savings, modelled on best private-sector practices, in order to serve national development goals.
But although African SWFs have already shown their effectiveness, their potential remains largely untapped. By mobilising and leveraging national savings, SWFs not only can increase governments’ capacity to finance public policies but also can help to attract more foreign capital. Above all, African SWFs can set an example by demonstrating governments’ commitment to their own economies: if we do not invest in our strategic infrastructure, industries, or social sectors, how can we expect others to come and do it for us?
We are convinced that our national savings can also be mobilised to integrate African economies into global capital flows. In recent years, African SWFs have demonstrated their capacity to implement innovative mechanisms such as public-private partnerships in the utilities, roads, ports, airports, telecoms-infrastructure, and health-care sectors. And they are agile enough to do much more, such as securitising state assets or using leaseback arrangements to fund public entities. All we need is our governments’ willingness to make full use of their SWFs.
Besides showcasing investment opportunities, our institutions know how to implement projects complying with environmental, social, and governance norms that are aligned with the United Nations 2030 Agenda for Sustainable Development. Last year, for example, African SWFs made strong commitments in the health sector. FGIS, the Gabonese Strategic Investment Fund, took over the country’s National Pharmaceutical Office, while the Nigeria Sovereign Investment Authority forged a partnership with the US nongovernmental organisation BIO Ventures for Global Health aimed at strengthening cancer research.
In this context, we are also calling for an institutional framework that encourages greater collaboration among African SWFs in order to pool our resources and projects. Such cooperation can further encourage African governments and international partners to use these funds to bolster the continent’s financial sovereignty. The Paris summit will help Africa, but, above all, we must help ourselves.
PUBLISHED ON
May 23,2021 [ VOL
22 , NO
1099]

Fortune News | Oct 16,2021

Viewpoints | Jun 12,2021

Commentaries | Jul 22,2023

Fortune News | May 26,2021

Fortune News | Apr 16,2022

Radar | Jul 11,2021

Radar | Aug 21,2021

Viewpoints | May 21,2022

Fortune News | May 23,2021

Fortune News | Nov 15,2018

Photo Gallery | 175496 Views | May 06,2019

Photo Gallery | 165718 Views | Apr 26,2019

Photo Gallery | 156067 Views | Oct 06,2021

My Opinion | 136824 Views | Aug 14,2021

Dec 22 , 2024 . By TIZITA SHEWAFERAW
Charged with transforming colossal state-owned enterprises into modern and competitiv...

Aug 18 , 2024 . By AKSAH ITALO
Although predictable Yonas Zerihun's job in the ride-hailing service is not immune to...

Jul 28 , 2024 . By TIZITA SHEWAFERAW
Unhabitual, perhaps too many, Samuel Gebreyohannes, 38, used to occasionally enjoy a couple of beers at breakfast. However, he recently swit...

Jul 13 , 2024 . By AKSAH ITALO
Investors who rely on tractors, trucks, and field vehicles for commuting, transporting commodities, and f...

Oct 18 , 2025
The political establishment, notably the ruling party and its top brass, has become p...

Oct 11 , 2025
Ladislas Farago, a roving Associated Press (AP) correspondent, arrived in Ethiopia in...

Oct 4 , 2025
Eyob Tekalegn (PhD) had been in the Governor's chair for only weeks when, on Septembe...
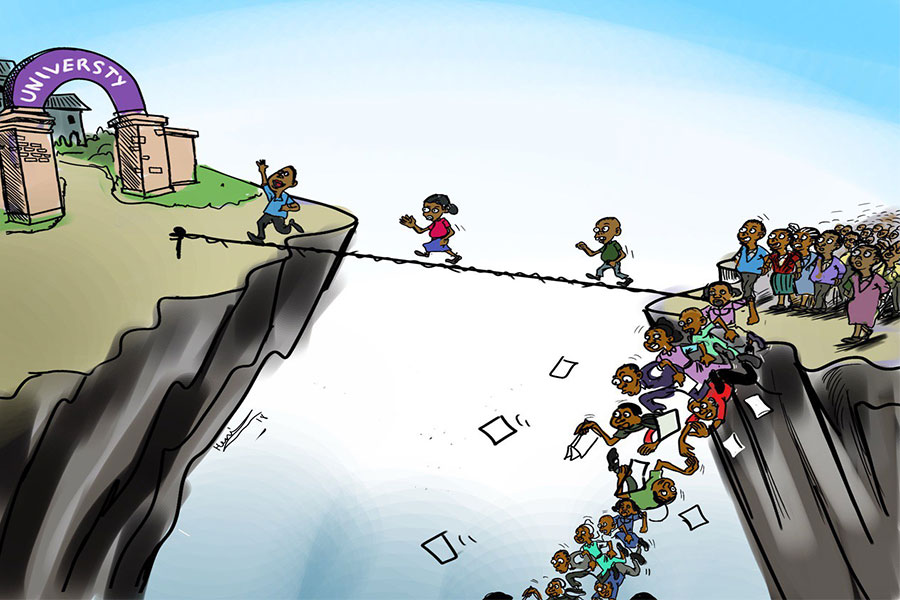
Sep 27 , 2025
Four years into an experiment with “shock therapy” in education, the national moo...
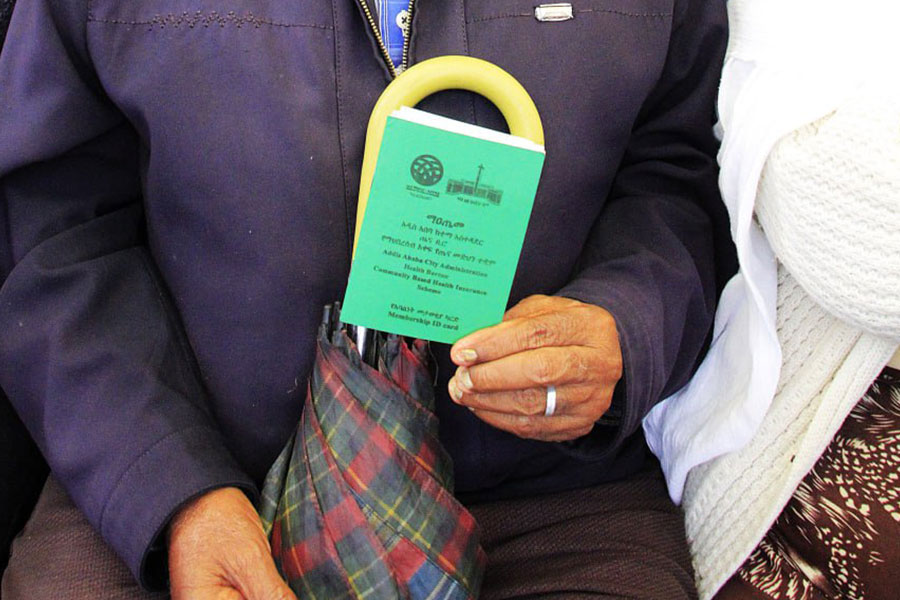

Oct 18 , 2025 . By NAHOM AYELE
In a sweeping reform that upends nearly a decade of uniform health insurance contribu...

Oct 18 , 2025 . By BEZAWIT HULUAGER
A bill that could transform the nutritional state sits in a limbo, even as the countr...

Oct 18 , 2025 . By SURAFEL MULUGETA
A long-planned directive to curb carbon emissions from fossil-fuel-powered vehicles h...

Oct 18 , 2025 . By BEZAWIT HULUAGER
Transaction advisors working with companies that hold over a quarter of a billion Bir...