
Fortune News | Aug 12,2023
Jan 7 , 2023
By Bekan Bekele
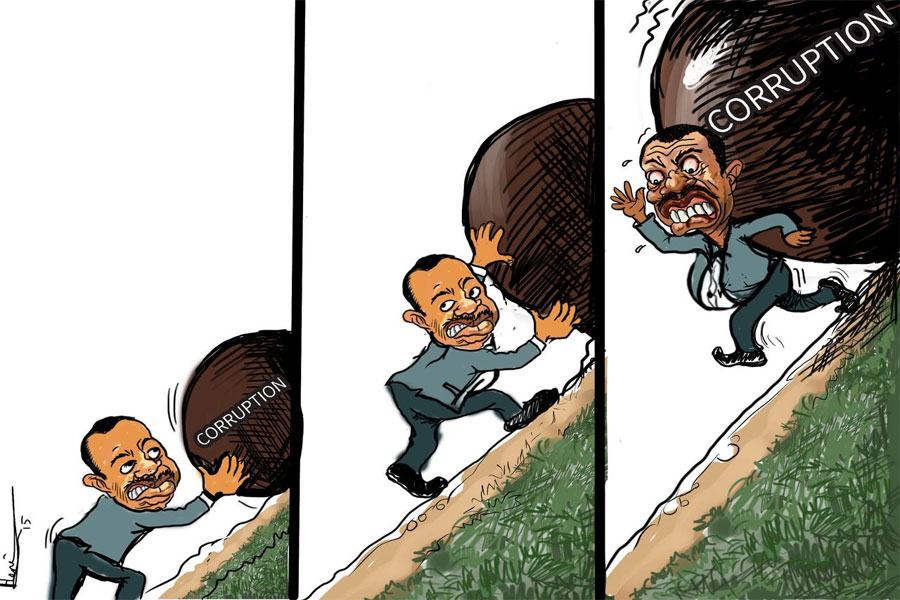
Corruption, typically involving bribery, is not a new concept in the world. According to World Economic Forum, it costs developing countries 1.26 trillion dollars annually. The figure roughly took two percent of the global GDP. It seeps from low-level public servants accepting petty bribes to national leaders stealing millions of dollars.
In developing countries such as Ethiopia, morality is not the main problem. It leads to an uneven distribution of wealth when the small business sector faces unfair competition from larger companies having an established illegal connection with government officials. Through this network, an inefficient allocation of resources persists, unqualified companies get the contracts, and poor quality of infrastructural development could lower the overall living standard of the populace.
It occurs when a specific individual, government official, or organisation exploits illegitimate means of maximising their personal or commercial benefits with the ability to elicit whatever means available.
Global Infrastructure Anti-Corruption Center (GIACC) has outlined some possible factors that facilitate the practice. According to GIACC, the nature of infrastructural projects under a complex contractual structure with diverse involvement lacks transparency. The extent of government involvement is greater with the absence of anti-corruption measures.
In developed and developing countries, officials' involvement in the practice is undeniable. Such involvement may occur when political figures extort bribes or require projects to be carried out for personal benefit. These problems are reinforced when a consistent anti-corruption policy is missing within the governmental system. Insufficient reporting of prosecution and the vulnerability of project owners' to bribery is considered significant factor for the misdeed.
Corruption is complex and encompasses a multitude of variables.
The political and economic environment can influence corruption. The more a country's economic activity is regulated and restricted, the greater the authorities' decision-making to circumvent bribery. Ineffective and unclear regulations invite regular individuals to pay bribes to speed up the bureaucratic processes. Exceptionality in regulations gives discretionary power to officials the potential to involve more.
A low wage has been one of the leading causes of corruption. The socioeconomic status of officials is a factor, as they can no longer control the effect due to their lower income. It is strongly influenced by the low salaries of public sector employees or state officials who try to improve their financial situation through bribes.
Job satisfaction has often been cited as a significant cause. A public employee's salary level influences the acceptance of bribes; the higher the salary level, the less likely a person is to be corrupt. But, it is tough to determine if higher wages reduce the range. The results of empirical studies in Africa have demonstrated the effects of higher salaries are either unclear or nonexistent.
Solving the issue of wages can only take the matter as far as a single solution. Most economists agree against salary top-ups because of the multi-faceted nature of corruption and its potential inflationary issues.
The central premise of increased wages would significantly value their position to the extent of bribes. Well-paid officials would not seek alternative sources of revenue. According to Transparency International, salary top-ups create distortions in the labour market, and the pay balance may create inflationary pressures affecting the macroeconomy. These distortions could make opportunistic behavior in governmental offices, ranging from nepotism of civil service reforms, which is crucial for public sector employees.
For any project to be practical implementing anti-corruption measures is necessary, together with the enforcement of robust investigation and prosecution of the corrupt. The lack of a coordinated approach prohibits steps from addressing the issue..
PUBLISHED ON
Jan 07,2023 [ VOL
23 , NO
1184]


Fortune News | Aug 12,2023

Verbatim | Jul 02,2022
View From Arada | Dec 24,2022

Editorial | Dec 31,2022
Editorial | Apr 03,2021

Sponsored Contents | Oct 25,2021

Radar | Dec 28,2019

Commentaries | Jun 25,2022

Fortune News | Apr 13,2019

Sunday with Eden | Dec 31,2022

My Opinion | 132272 Views | Aug 14,2021

My Opinion | 128692 Views | Aug 21,2021

My Opinion | 126600 Views | Sep 10,2021

My Opinion | 124206 Views | Aug 07,2021





Dec 22 , 2024 . By TIZITA SHEWAFERAW
Charged with transforming colossal state-owned enterprises into modern and competitiv...

Aug 18 , 2024 . By AKSAH ITALO
Although predictable Yonas Zerihun's job in the ride-hailing service is not immune to...

Jul 28 , 2024 . By TIZITA SHEWAFERAW
Unhabitual, perhaps too many, Samuel Gebreyohannes, 38, used to occasionally enjoy a couple of beers at breakfast. However, he recently swit...

Jul 13 , 2024 . By AKSAH ITALO
Investors who rely on tractors, trucks, and field vehicles for commuting, transporting commodities, and f...

Jul 12 , 2025
Political leaders and their policy advisors often promise great leaps forward, yet th...

Jul 5 , 2025
Six years ago, Ethiopia was the darling of international liberal commentators. A year...

Jun 28 , 2025
Meseret Damtie, the assertive auditor general, has never been shy about naming names...
Jun 21 , 2025
A well-worn adage says, “Budget is not destiny, but it is direction.” Examining t...

Jul 13 , 2025 . By YITBAREK GETACHEW
The Addis Abeba City Revenue Bureau has introduced a new directive set to reshape how...

Jul 13 , 2025 . By BEZAWIT HULUAGER
Addis Abeba has approved a record 350 billion Br budget for the 2025/26 fiscal year,...

Jul 13 , 2025 . By RUTH BERHANU
The Addis Abeba Revenue Bureau has scrapped a value-added tax (VAT) on unprocessed ve...

Jul 13 , 2025 . By NAHOM AYELE
Federal lawmakers have finally brought closure to a protracted and contentious tax de...