
Oct 26 , 2024
By Bogolo Kenewendo , Patrick Njoroge
A large-scale debt relief plan is necessary to relieve the crushing debt burden and enable investment in climate-resilient infrastructure. This plan should involve bilateral creditors and MDBs taking a 'haircut' to restore fiscal stability, incentives and penalties to ensure creditors' participation in debt restructuring, and support for non-distressed countries to reduce capital costs, write Bogolo Kenewendo and Patrick Njoroge, co-chairs of the Debt Relief for a Green & Inclusive Recovery Project. This commentary is provided by Project Syndicate (PS).
Many countries have experienced extreme weather in one form or another this year. The summer, marked by intense wildfires, was the hottest on record, while the return of El Nino has led to catastrophic flooding and other disasters. Such shocks demonstrate the urgent need for multilateral efforts to address climate change and achieve sustainable development.
In the last few months of this year, world leaders will gather for a series of summits – including the International Monetary Fund (IMF)-World Bank Group annual meetings in Washington, DC [ongoing], the G20 summit in Rio de Janeiro, and the United Nations Climate Change Conference (COP29) in Baku – where they could make progress on these fronts. These meetings are particularly important for African countries, which remain vulnerable to the effects of global warming amid a deepening sovereign debt crisis.
Of the 20 countries most vulnerable to climate change, 17 are in Africa. In addition to adverse weather and rising temperatures, African economies have suffered a series of external shocks in recent years, including inflation spikes, interest-rate hikes in advanced economies, rising geopolitical tensions, and violent conflicts. Partly due to these shocks, the continent’s public debt levels increased by a whopping 240pc between 2008 and 2022.
The consequences are dire. Over half of African countries now spend more on interest payments than on healthcare and lack the fiscal space to invest in sustainable development. This cycle of debt and development distress makes these countries even more vulnerable to the effects of global warming, trapping them in a loop of economic instability and environmental degradation.
While increased liquidity may offer temporary relief to African economies by easing short-term fiscal pressures, it fails to address the deeper debt problem impeding green growth. To mobilise the financing needed for climate action and to achieve the UN Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs) by 2030, we estimate that at least 34 African countries will require significant debt relief. Unfortunately, the G20’s Common Framework for Debt Treatments, designed to provide relief to countries in debt distress, has proven woefully inadequate.
Its case-by-case approach is slow and insufficient, leaving many countries in a perpetual state of fiscal instability. Private creditors’ reluctance to participate in debt restructuring, coupled with the exclusion of multilateral development banks (MDBs), has resulted in uneven and often inadequate responses.
To embark on the path of sustainable development, African countries need large-scale debt relief. This would provide governments with the fiscal space to invest in resilient infrastructure, renewable energy, and other climate-related projects. Without such measures, Africa’s green-growth aspirations will be unfulfilled, and the continent will continue to suffer from unsustainable debt dynamics that escalate climate damage and worsen social outcomes.
Large-scale debt relief should rest on three pillars.
Bilateral creditors and MDBs should take a haircut to restore fiscal stability in debtor countries. Incentives and penalties are also required to ensure private and commercial creditors’ full participation in debt restructuring. Finally, credit enhancements and support for non-distressed countries should be provided to reduce capital costs and maintain liquidity. This holistic approach would enable African countries to scale up and sustain investment in climate resilience and sustainable development.
An essential part of these reforms is the inclusion of climate considerations in the IMF’s debt sustainability analyses (DSA). Currently, DSAs focus on a country’s ability to service its debt, while failing to consider its need to invest in the energy transition and the industries of the future. By incorporating climate risks and opportunities into DSAs, the international community can ensure that debt relief is aligned with broader sustainability goals.
It is also critical for all creditor classes, including private bondholders and MDBs, to participate in debt restructuring. Using fair comparable-treatment rules to determine losses would ensure equitable burden-sharing.
Such a coordinated and comprehensive approach to debt relief would unlock Africa’s potential for green growth, an essential part of any long-term solution to the climate crisis. The continent has vast solar, wind, and hydro resources and the world’s youngest and fastest-growing workforce. With the right investments, Africa could become a hub for renewable energy and clean industries, thereby advancing the continent’s development goals and the global fight against climate change.
Looking ahead to 2025, African leaders will have a unique opportunity to drive the reforms needed to address the debt-climate nexus. With South Africa presiding over the G20 (which now counts the African Union as a permanent member), and Uganda leading the G77, the continent’s governments will be in a position to push for significant debt relief and critical reforms to the global financial architecture.
The climate and debt crises in Africa are inextricably linked, and addressing one but not the other is a recipe for failure. The international community should act now to support Africa in building a sustainable, green future for all.
PUBLISHED ON
Oct 26,2024 [ VOL
25 , NO
1278]

Radar | May 02,2020

Agenda | Oct 06,2024

Radar | Jul 17,2022

Exclusive Interviews | May 17,2025
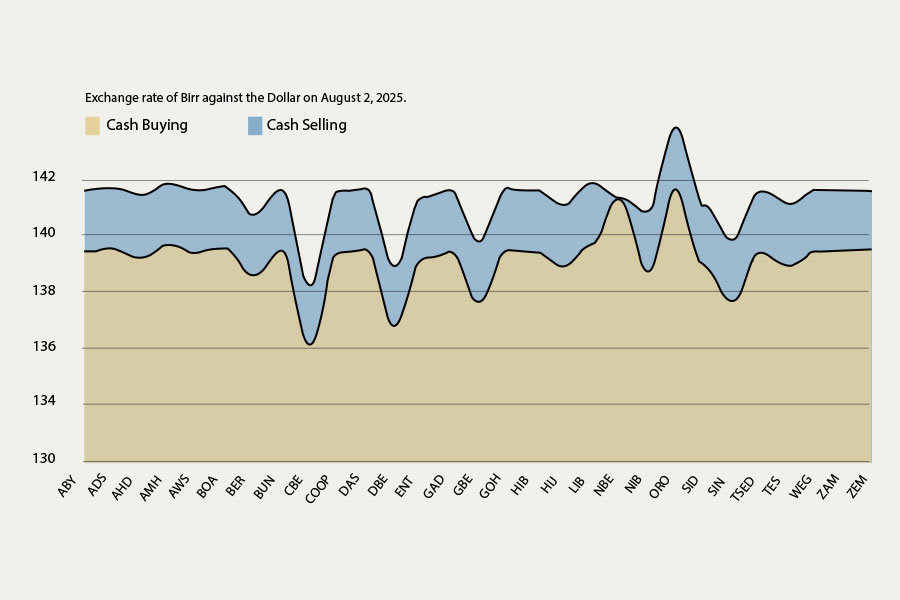
Money Market Watch | Aug 17,2025

Radar | Jun 30,2024

Commentaries | Apr 17,2020

Viewpoints | Oct 20,2024

Viewpoints | Jun 14,2025

My Opinion | Oct 05,2024

Photo Gallery | 167111 Views | May 06,2019

Photo Gallery | 157357 Views | Apr 26,2019

Photo Gallery | 146638 Views | Oct 06,2021

My Opinion | 135984 Views | Aug 14,2021

Dec 22 , 2024 . By TIZITA SHEWAFERAW
Charged with transforming colossal state-owned enterprises into modern and competitiv...

Aug 18 , 2024 . By AKSAH ITALO
Although predictable Yonas Zerihun's job in the ride-hailing service is not immune to...

Jul 28 , 2024 . By TIZITA SHEWAFERAW
Unhabitual, perhaps too many, Samuel Gebreyohannes, 38, used to occasionally enjoy a couple of beers at breakfast. However, he recently swit...

Jul 13 , 2024 . By AKSAH ITALO
Investors who rely on tractors, trucks, and field vehicles for commuting, transporting commodities, and f...
Sep 27 , 2025
Four years into an experiment with “shock therapy” in education, the national moo...
Sep 20 , 2025
Getachew Reda's return to the national stage was always going to stir attention. Once...

Sep 13 , 2025
At its launch in Nairobi two years ago, the Africa Climate Summit was billed as the f...

Sep 6 , 2025
The dawn of a new year is more than a simple turning of the calendar. It is a moment...

Sep 27 , 2025
Meskel Square turned into a rolling wave of colour and sound on Friday, September 26, 2025, as thousands pressed toward the annual bonfire c...

Sep 27 , 2025 . By YITBAREK GETACHEW
Unity University has increased tuition fees sharply, jolting students and families alike, drawing critici...

Sep 27 , 2025 . By BEZAWIT HULUAGER
Seventeen years after its inception as a flagship market reform for agricultural modernisation, the Ethio...

Sep 27 , 2025 . By BEZAWIT HULUAGER
The elevator industry is bracing for sweeping reforms as construction regulators are to impose the first...