
Commentaries | May 13,2023
Jul 30 , 2022
By Anne O. Krueger
A tragedy is unfolding in Sri Lanka. Citizens must queue for food and pharmaceuticals, vehicle owners cannot fill their tanks, and there have been rolling power outages. The economy is paralysed, and because the country’s debts are already unsustainable, it cannot borrow. The country is suffering the world’s worst economic crisis since World War II.
The situation is so dire that millions of people have taken to the streets. The president has fled the country, and now parliament has elected a new, but unpopular, replacement. If all goes smoothly (a big "if" given the events of recent weeks), the International Monetary Fund (IMF) can come to Sri Lanka’s aid with a rescue loan package (allowing for the purchase of essential imports) and a programme to achieve sustainable fiscal, monetary, and exchange-rate policies.
Sri Lanka’s plight serves as a lesson to other governments. When a country’s economic problems are obviously becoming insurmountable, postponing a reckoning through various piecemeal measures will only make matters worse in the end.
For years, Sri Lanka was a “donor darling,” owing to its relatively high standard of living, good social services, and robust economic growth. In the first half of the last decade, it boasted a 6.5pc average annual growth rate – one of the world’s highest – and very low population growth. Though economic growth slowed after 2015, it still averaged well over three percent through 2019.
But at the end of that year, a new government came to power and immediately announced a large tax cut. In both 2020 and 2021, the government ran a fiscal deficit of more than 10pc of GDP. The annual inflation rate rose from an average of under five percent in previous years to 39.1pc in May, and then to 54.6pc in June.
Worse, even with inflation already accelerating, the government announced in the spring of 2021 that it was banning all chemical-fertiliser imports. Predictably, rice production fell by 20pc, tea exports fell to their lowest level in more than two decades, and more than one-third of the country’s farmland was left fallow.
The COVID-19 pandemic came on top of these self-inflicted wounds, causing a sharp decline in tourist revenues, which then deepened Sri Lanka’s foreign-exchange shortage and further curtailed its ability to purchase imports. By late 2021, the situation was spinning out of control; and in May, the government defaulted on its foreign debt.
Now, Sri Lanka cannot obtain essential inputs to restart the economy until it has restructured its debt and installed a working government. Restructuring the country’s debt will be unusually complicated because a significant portion is owed to China, which does not participate in the multilateral Western-led restructuring exercises for overly indebted sovereign borrowers.
Again, the lesson for other debt-distressed countries is clear. While a country’s economic authorities can delay some of the consequences of ill-advised policies for a while through import rationing and prohibitions, price controls, fiscal deficits, foreign borrowing, and printing money, the music eventually will stop. When a government’s only remaining choice is to implement serious reforms or pursue desperate and economically irrational measures, doing the latter will merely deepen the misery and human suffering caused by the earlier policy mistakes.
Had Sri Lanka approached the IMF late in 2021 (or even earlier) and implemented the painful reforms needed to rein in inflation and reduce its current-account and fiscal deficits, at least six months of suffering could have been avoided. The country’s external debt would not have risen quite so high, and the road to recovery would not have been quite so long. More to the point, the country’s descent into complete political chaos might have been avoided altogether.
Since the start of the pandemic, the international community has appropriately been directing more attention to the plight of heavily indebted developing countries, with the G20 rolling out a Debt Service Suspension Initiative that extended some 13 billion dollars of relief to 48 countries in 2020-21, but that was a drop in the bucket relative to needs.
Worse, there has been very little differentiation between countries whose underlying economic policies were sustainable and those whose policies would have become unsustainable without reform, even in the absence of COVID-19. Lending to a country in the latter category without ensuring that it has or will implement sustainable economic policies is not doing it any favours. On the contrary, such “support” merely postpones the day of reckoning and leaves it with an even higher debt-service burden when the time comes.
Policymakers in other economically struggling countries should take heed of Sri Lanka’s tale. The lessons can be paired with those from Brazil, which, following its 2002 debt crisis, quickly adopted the necessary policy reforms and went on to enjoy years of sustained growth. Brazil, too, had a choice between swift painful action to create the conditions for recovery, and denial and delay to put off the inevitable. Its leaders proved wiser than those who have since high-tailed it out of Sri Lanka.
PUBLISHED ON
Jul 30,2022 [ VOL
23 , NO
1161]


Commentaries | May 13,2023
Editorial | Jul 10,2020

Editorial | Oct 15,2022

Commentaries | Apr 11,2020

My Opinion | Jan 31,2021


Commentaries | Mar 27,2021

Viewpoints | Apr 20,2019

Viewpoints | Feb 16,2019

Commentaries | Jan 31,2021

Photo Gallery | 157232 Views | May 06,2019

Photo Gallery | 147517 Views | Apr 26,2019

Photo Gallery | 136112 Views | Oct 06,2021

My Opinion | 135300 Views | Aug 14,2021

Dec 22 , 2024 . By TIZITA SHEWAFERAW
Charged with transforming colossal state-owned enterprises into modern and competitiv...

Aug 18 , 2024 . By AKSAH ITALO
Although predictable Yonas Zerihun's job in the ride-hailing service is not immune to...

Jul 28 , 2024 . By TIZITA SHEWAFERAW
Unhabitual, perhaps too many, Samuel Gebreyohannes, 38, used to occasionally enjoy a couple of beers at breakfast. However, he recently swit...

Jul 13 , 2024 . By AKSAH ITALO
Investors who rely on tractors, trucks, and field vehicles for commuting, transporting commodities, and f...

Sep 13 , 2025
At its launch in Nairobi two years ago, the Africa Climate Summit was billed as the f...

Sep 6 , 2025
The dawn of a new year is more than a simple turning of the calendar. It is a moment...

Aug 30 , 2025
For Germans, Otto von Bismarck is first remembered as the architect of a unified nati...
Aug 23 , 2025
Banks have a new obsession. After decades chasing deposits and, more recently, digita...
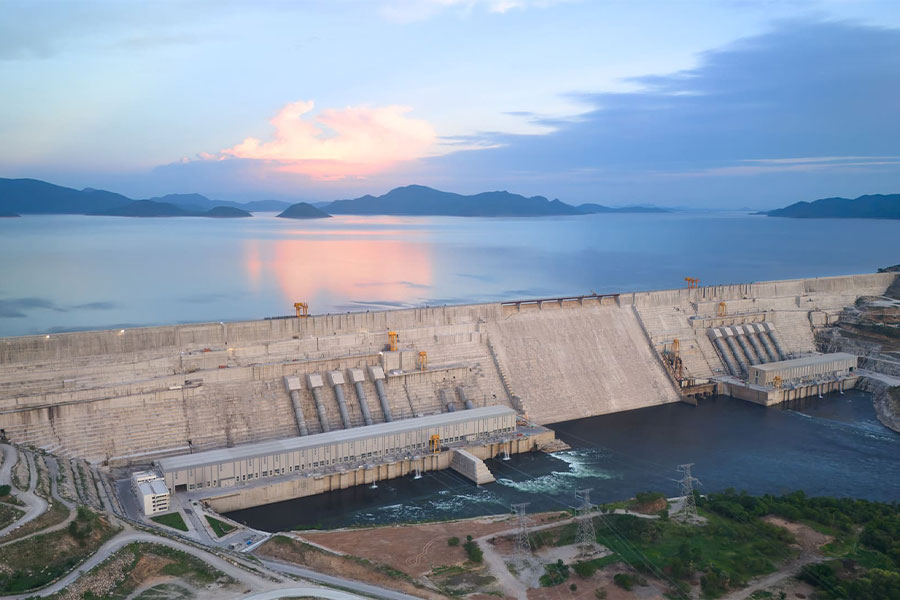

Sep 15 , 2025 . By AMANUEL BEKELE
The Grand Ethiopian Renaissance Dam (GERD), Africa's largest hydroelectric power proj...

Sep 13 , 2025
The initial budget in 2011 was 80 billion Br, but this figure swelled to a revised cost of 240 billion Br by 2024, a challenge that was exac...

Banks are facing growing pressure to make sustainability central to their operations as regulators and in...

Sep 15 , 2025 . By YITBAREK GETACHEW
The Addis Abeba City Cabinet has enacted a landmark reform to its long-contentious setback regulations, a...