
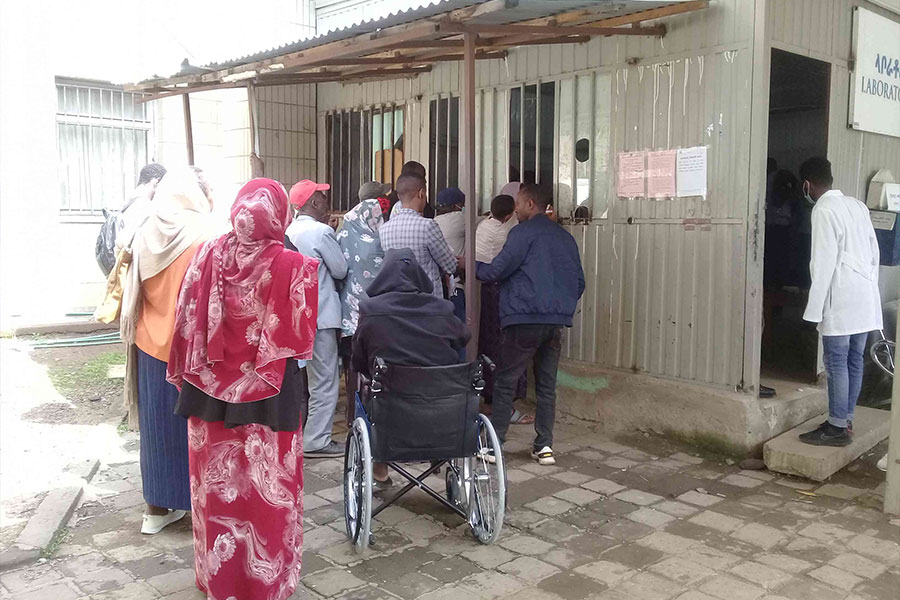
On any day, the waiting hall of Black Lion Hospital is not a sight for the faint-hearted. Patients seeking treatment find themselves marooned on multi-seat waiting chairs in dangerously close quarters and unsanitary conditions.
But even this has changed, with patients wary of visiting health centres and public health professionals themselves trying to devise ways of limiting the number of patients that come to hospitals.
Black Lion, for instance, used to have an average of 20,000 patients a day seeking its services before the outbreak of COVID-19. By April, there was only a fifth as many, with people attempting to avoid contracting the virus and decreasing their mobility throughout Addis Abeba.
It was this fear of slacking health services that induced the establishment of the Essential Services Continuity Section under the COVID-19 inter-ministerial task force being led by the Prime Minister. Its mandate included monitoring health institutions for non-COVID-19 healthcare.
Among the practices being expanded is telehealth, where patients are advised by their doctors over the phone under guidelines provided by the Health Ministry. But with doctor’s visits now being spaced out widely, those considered high-risk have been impacted detrimentally. Some patients have died before their next appointment.
It is still not clear if such non-COVID-19 related deaths have been on the rise given poor record-keeping in the country. At the moment, assessments done until the end of May show no significant changes in death rates in Addis Abeba. The tally for June and July are still to come.
You can read the full story here
PUBLISHED ON
Aug 08,2020 [ VOL
21 , NO
1058]

Viewpoints | Oct 24,2020

Agenda | Jun 17,2023

Fortune News | Aug 12,2023

Viewpoints | Sep 17,2022

Radar | Jul 02,2022

Radar | Mar 05,2022


Fortune News | Dec 19,2020

Fortune News | Jul 26,2025

Fortune News | Mar 13,2021

Dec 22 , 2024 . By TIZITA SHEWAFERAW
Charged with transforming colossal state-owned enterprises into modern and competitiv...

Aug 18 , 2024 . By AKSAH ITALO
Although predictable Yonas Zerihun's job in the ride-hailing service is not immune to...

Jul 28 , 2024 . By TIZITA SHEWAFERAW
Unhabitual, perhaps too many, Samuel Gebreyohannes, 38, used to occasionally enjoy a couple of beers at breakfast. However, he recently swit...

Jul 13 , 2024 . By AKSAH ITALO
Investors who rely on tractors, trucks, and field vehicles for commuting, transporting commodities, and f...

Oct 11 , 2025
Ladislas Farago, a roving Associated Press (AP) correspondent, arrived in Ethiopia in...

Oct 4 , 2025
Eyob Tekalegn (PhD) had been in the Governor's chair for only weeks when, on Septembe...
Sep 27 , 2025
Four years into an experiment with “shock therapy” in education, the national moo...
Sep 20 , 2025
Getachew Reda's return to the national stage was always going to stir attention. Once...