
My Opinion | Jul 15,2023
Jun 19 , 2021
By Christian Tesfaye
Lately, coffee has been good for Ethiopia. Over the past three months, exports have been showing impressive growth, fetching 107 million dollars in March. The month after that, this reached 114 million dollars. In May, it outperformed records with 131 million dollars worth of coffee exported to the international market.
What is going on?
Characteristically, the authorities would say that it is more effective agricultural and supply chain policies. Indeed, the volume of the commodity being exported has increased. But it has more to do with the fact that every single bag of coffee beans is selling for higher than it used to last year—a consequence of providence.
Or, in Brazil’s case, bad luck. The South American giant is going through a drought, and as the biggest exporter of the bean in the world, there is currently a global coffee shortage. Arabica coffee is now selling for its highest price since 2016, according to Business Insider.
“Coffee prices [on average of all time] have risen nearly 70pc in the past year and currently trade around 1.66 dollars per pound,” reported the financial and business news outlet.
If the drought lasts through August, it bodes terribly for Brazil over the next year, but Ethiopian coffee producers have cause to celebrate. And, hey, it is not like Brazil, while a world leader in the export of the commodity, will have its economy hampered solely by this. It is an economy that has diversified, unlike Ethiopia.
But this is just one side of the story of global inflation and its impact on this country. It is not just a drought in Brazil that is pushing the global prices of goods and services. The primary driver is the United States. The Biden administration’s multi-trillion-dollar economic stimulus package is helping the country and the world recover rapidly from the pandemic-induced global recession. Unfortunately, it is also proving the Miltonian argument that increasing money supply is inherently inflationary, even for the US—the price of goods and services is increasing in the country, although it is yet to be seen if it is lasting.
Making matters worse is that as the global economy recovers and demand increases, supply is not catching up. Commodities such as lumber and copper are all rising. A shortage of semiconductor chips is impacting the production of devices that use electronic equipment, from cars to computers and smartphones.
More importantly for Ethiopia, there is a crippling shortage of shipping containers, also as a result of COVID-19. How this became a problem is too convoluted to explain here but let us just say that the uneven easing of restrictions across the world has meant that many containers are held up in all the wrong places.
When it comes to Ethiopia, this translates to the state monopoly Ethiopian Shipping & Logistics Service Enterprise tripling, in some cases, its shipping prices. The Enterprise is trying to lease or buy more containers, but fat chance it has as every shipping company worldwide is trying to do the same—a costly bidding war.
Just as a global chip shortage has meant that laptops and computers are more expensive—of course, only one factor among many, like the depreciation of the Birr—higher shipping tariffs mean that products would get more expensive here. Importers, manufacturers, distributors and retailers would transfer the inflated prices to consumers; a price for being a member, albeit tiny and mostly insignificant, of the global economy.
PUBLISHED ON
Jun 19,2021 [ VOL
22 , NO
1103]


My Opinion | Jul 15,2023

Featured | Mar 07,2020

Viewpoints | Jun 28,2025

Viewpoints | Apr 22,2022

Commentaries | Oct 28,2023

Radar | Aug 17,2025

View From Arada | Apr 11,2020

Commentaries | Mar 11,2023

Fortune News | Aug 28,2021

My Opinion | Apr 01,2023

Photo Gallery | 175732 Views | May 06,2019

Photo Gallery | 165951 Views | Apr 26,2019

Photo Gallery | 156344 Views | Oct 06,2021

My Opinion | 136844 Views | Aug 14,2021

Dec 22 , 2024 . By TIZITA SHEWAFERAW
Charged with transforming colossal state-owned enterprises into modern and competitiv...

Aug 18 , 2024 . By AKSAH ITALO
Although predictable Yonas Zerihun's job in the ride-hailing service is not immune to...

Jul 28 , 2024 . By TIZITA SHEWAFERAW
Unhabitual, perhaps too many, Samuel Gebreyohannes, 38, used to occasionally enjoy a couple of beers at breakfast. However, he recently swit...

Jul 13 , 2024 . By AKSAH ITALO
Investors who rely on tractors, trucks, and field vehicles for commuting, transporting commodities, and f...

Oct 18 , 2025
The political establishment, notably the ruling party and its top brass, has become p...

Oct 11 , 2025
Ladislas Farago, a roving Associated Press (AP) correspondent, arrived in Ethiopia in...

Oct 4 , 2025
Eyob Tekalegn (PhD) had been in the Governor's chair for only weeks when, on Septembe...
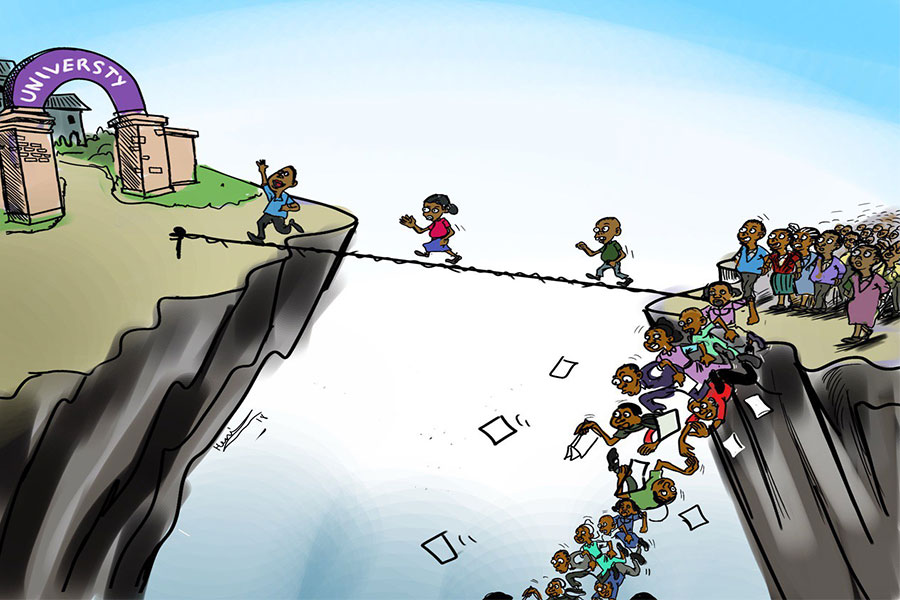
Sep 27 , 2025
Four years into an experiment with “shock therapy” in education, the national moo...

Oct 18 , 2025 . By NAHOM AYELE
In a sweeping reform that upends nearly a decade of uniform health insurance contribu...

A bill that could transform the nutritional state sits in a limbo, even as the countr...

Oct 18 , 2025 . By SURAFEL MULUGETA
A long-planned directive to curb carbon emissions from fossil-fuel-powered vehicles h...

Oct 18 , 2025 . By BEZAWIT HULUAGER
Transaction advisors working with companies that hold over a quarter of a billion Bir...