
Commentaries | Mar 11,2023
Sep 28 , 2019
By Nouriel Roubini
In the classic game of “chicken,” two drivers race directly toward each other, and the first to swerve is the “loser.” If neither swerves, both will probably die. In the past, such scenarios have been studied to assess the risks posed by great power rivalries. In the case of the Cuban missile crisis, for example, Soviet and American leaders were confronted with the choice of losing face or risking a catastrophic collision. The question, always, is whether a compromise can be found that spares both parties their lives and their credibility.
There are now several geo-economic games of chicken playing out. In each case, failure to compromise would lead to a collision, most likely followed by a global recession and financial crisis. The first and most important contest is between the United States and China over trade and technology. The second is the brewing dispute between the US and Iran. In Europe, there is the escalating brinkmanship between British Prime Minister Boris Johnson and the European Union over Brexit. Finally, there is Argentina, which could end up on a collision course with the International Monetary Fund after the likely victory of the Peronist Alberto Fernández in next month’s presidential election.
In the first case, a full-scale trade, currency, tech and cold war between the US and China would push the current downturn in manufacturing, trade and capital spending into services and private consumption, tipping the US and global economies into a severe recession. Similarly, a military conflict between the US and Iran would drive oil prices above 100 dollars per barrel, triggering stagflation (a recession with rising inflation). That, after all, is what happened in 1973 during the Yom Kippur War, in 1979 following the Iranian Revolution, and in 1990 after Iraq’s invasion of Kuwait.
A blowup over Brexit might not by itself cause a global recession, but it would certainly trigger a European one, which would then spill over to other economies. The conventional wisdom is that a “hard” Brexit would lead to a severe recession in the United Kingdom but not in Europe, because the UK is more reliant on trade with the EU than vice versa. This is naive. The Eurozone is already suffering a sharp slowdown and is in the grip of a manufacturing recession; and the Netherlands, Belgium, Ireland, and Germany – which is nearing a recession – do in fact rely heavily on the UK export market.
With Eurozone business confidence already depressed as a result of Sino-American trade tensions, a chaotic Brexit would be the last straw. Just imagine thousands of trucks and cars lining up to fill out new customs paperwork in Dover and Calais. Moreover, a European recession would have knock-on effects, undercutting growth globally and possibly triggering a risk-off episode. It could even lead to new currency wars, if the value of the euro and pound were to fall too sharply against other currencies (not least the US dollar).
A crisis in Argentina could also have global consequences. If Fernández defeats President Mauricio Macri and then scuttles the country’s 57-billion-dollar IMF programme, Argentina could suffer a repeat of its 2001 currency crisis and default. That could lead to capital flight from emerging markets more generally, possibly triggering crises in highly indebted Turkey, Venezuela, Pakistan and Lebanon, and further complicating matters for India, South Africa, China, Brazil, Mexico and Ecuador.
In all four scenarios, both sides want to save face. US President Donald Trump wants a deal with China, in order to stabilise the economy and markets before his re-election bid in 2020; Chinese President Xi Jinping also wants a deal to halt China’s slowdown. But neither wants to be the “chicken,” because that would undermine their domestic political standing and empower the other side. Still, without a deal by year’s end, a collision will become likely. As the clock ticks down, a bad outcome becomes more likely.
Similarly, Trump thought he could bully Iran by abandoning the Joint Comprehensive Plan of Action and imposing severe sanctions. But the Iranians have responded by escalating their regional provocations, knowing full well that Trump cannot afford a full-scale war and the oil-price spike that would result from it. Moreover, Iran does not want to enter negotiations that would give Trump a photo opportunity until some sanctions are lifted. With both sides reluctant to blink first – and with both Saudi Arabia and Israel egging on the Trump administration – the risk of an accident is rising.
Having perhaps been inspired by Trump, Johnson naively thought that he could use the threat of a hard Brexit to bully the EU into offering a better exit deal than what his predecessor had secured. But now that Parliament has passed legislation to prevent a hard Brexit, Johnson is playing two games of chicken at once. A compromise with the EU on the Irish “backstop” is still possible before the October 31 deadline, but the probability of a de facto hard-Brexit scenario is also increasing.
In Argentina, both sides are posturing. Fernández wants a clear electoral mandate and is campaigning on the message that Macri and the IMF are to blame for all the country’s problems. The IMF’s leverage is obvious: if it permanently withholds the next 5.4-billion-dollar tranche of funding and ends the bailout, Argentina will suffer another financial collapse. But Fernández has leverage, too, because a 57-billion-dollar debt is a problem for any creditor; the IMF’s ability to help other distressed economies would be constrained by an Argentinean collapse. As in the other cases, a face-saving compromise is better for all, but a collision and financial meltdown cannot be ruled out.
The problem is that while compromise requires both parties to de-escalate, the tactical logic of chicken rewards crazy behavior. If I can make it look like I have removed my steering wheel, the other side will have no choice but to swerve. But if both sides throw out their steering wheels, a collision becomes unavoidable.
The good news is that in the four scenarios above, each side is still talking to the other, or may be open to dialogue under some face-saving conditions. The bad news is that all sides are still very far from any kind of agreement. Worse, there are big egos in the mix, some of whom might prefer to crash than be perceived as a chicken. The future of the global economy thus hinges on four games of daring that could go either way.
PUBLISHED ON
Sep 28,2019 [ VOL
20 , NO
1013]


Commentaries | Mar 11,2023

Commentaries | Jun 18,2022

Viewpoints | Aug 19,2023

My Opinion | Jun 29,2024

Fortune News | Nov 03,2024

Fortune News | Nov 24, 2024
Editorial | Jun 21,2025

Commentaries | Dec 30,2023

View From Arada | Sep 27,2025

Fortune News | Jan 05,2019

Photo Gallery | 177259 Views | May 06,2019

Photo Gallery | 167466 Views | Apr 26,2019

Photo Gallery | 158104 Views | Oct 06,2021

My Opinion | 136976 Views | Aug 14,2021
Commentaries | Oct 25,2025

Dec 22 , 2024 . By TIZITA SHEWAFERAW
Charged with transforming colossal state-owned enterprises into modern and competitiv...

Aug 18 , 2024 . By AKSAH ITALO
Although predictable Yonas Zerihun's job in the ride-hailing service is not immune to...

Jul 28 , 2024 . By TIZITA SHEWAFERAW
Unhabitual, perhaps too many, Samuel Gebreyohannes, 38, used to occasionally enjoy a couple of beers at breakfast. However, he recently swit...

Jul 13 , 2024 . By AKSAH ITALO
Investors who rely on tractors, trucks, and field vehicles for commuting, transporting commodities, and f...

Oct 25 , 2025
The regulatory machinery is on overdrive. In only two years, no fewer than 35 new pro...

Oct 18 , 2025
The political establishment, notably the ruling party and its top brass, has become p...

Oct 11 , 2025
Ladislas Farago, a roving Associated Press (AP) correspondent, arrived in Ethiopia in...

Oct 4 , 2025
Eyob Tekalegn (PhD) had been in the Governor's chair for only weeks when, on Septembe...

Oct 25 , 2025 . By YITBAREK GETACHEW
Officials of the Addis Abeba's Education Bureau have embarked on an ambitious experim...

Oct 26 , 2025 . By YITBAREK GETACHEW
The federal government is making a landmark shift in its investment incentive regime...

Oct 26 , 2025 . By NAHOM AYELE
The National Bank of Ethiopia (NBE) is preparing to issue a directive that will funda...
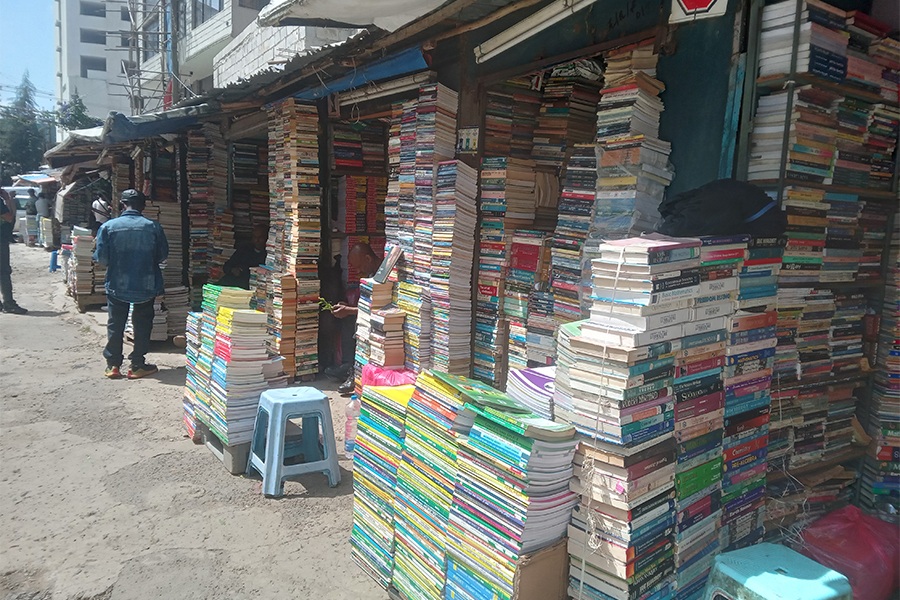

Oct 26 , 2025 . By SURAFEL MULUGETA
A community of booksellers shadowing the Ethiopian National Theatre has been jolted b...