
Aug 28 , 2021
By Adesuwa Ifedi
The COVID-19 pandemic has dealt a severe blow to Africa's people and economies, but across the continent, communities and nations are on the rebound. To truly succeed, this economic comeback will need to create millions of jobs for Africa's booming youth population. African policymakers and business leaders must look to agriculture – a sector of vast and still untapped resources – to secure a productive and sustainable future for food.
There have been lots of dire warnings about the food situation in Africa, and there are indeed many reasons to be concerned. The COVID-19 pandemic disrupted supply chains, upending many farmers’ precarious livelihoods that are already being hit hard by the climate crisis in new and unsettling ways. It is easy to think that we are on an unalterable path toward a crisis of food security in Africa – but it does not have to be the case.
The future of food in Africa is in the hands of African farmers – particularly our young farmers, of whom we are in desperately short supply. About 60pc of Africans are under 25 years old, but the average age of an African smallholder farmer is over 60. Too many young Africans view farming as exhausting work with antiquated tools for very low pay. One rarely hears an African under 30 say, “I want to be a farmer.” And many parents shudder at the thought of their children going into farming.
If we are going to secure a sustainable future of food in Africa, these things need to change. We need to show agriculture can be a major source of jobs for the future.
Heifer International [where the author is a vice-president] released a report this month revealing why youth are turning away from agriculture. It also highlights a major opportunity to evolve the sector and bring them back. The survey, which drew responses from some 30,000 young Africans across 11 countries, found that only about one in four young farmers has access to the kinds of agricultural technologies that are transforming food production around the world.
These “agritech” tools include things like digital sensors that monitor soil health and digital platforms that connect farmers with market opportunities, technical advice and high-quality inputs. The fact that many young African farmers lack access to these kinds of tools puts them at a severe disadvantage.
We also found that with the appropriate financing, training and access to technologies, many more African youth would seriously consider pursuing a career in agriculture. The survey, which included focus groups with farmers and tech companies, revealed evidence of a rapidly growing cadre of agritech start-ups operated by creative, young Africans across the continent. By encouraging and supporting this new generation of agritech innovators, we can boost access to labour-saving and transformative technologies for huge numbers of smallholder farmers across Africa.
These young, innovative entrepreneurs understand the farming struggles of their parents’ generation. But they also believe farming can provide a promising future for their generation. In Ethiopia, a group of young engineers is providing drone services for analysing farm performance and a mobile application to help farmers detect crop disease. A start-up in Nigeria is using machine learning to guide farmers from seed to market – helping them choose what to grow, how to grow it and where to sell it. Farmers from Senegal to Kenya can sign on to receive SMS alerts on important weather updates, market insights and farming advice.
With these kinds of tools and technologies, young African farmers could better manage, or even avoid, many of the challenges they reported in the survey, from climate shocks to crop pests and disease. These technologies have the power to make smallholder farmers much more productive, profitable and sustainable – and to make food production more exciting and attractive for a new generation.
Financing and supporting these companies are powerful ways of creating a virtuous circle in African agriculture: successful youth-led agritech companies lead to more successful young farmers and a more dynamic and profitable agricultural sector. Their success then creates an even bigger market opportunity for agriculture innovators that encourages more investors to get involved.
But this future will not just magically appear. Governments and businesses alike need to invest in African farmers and encourage them to develop and adopt agritech innovations. The need for this investment grows more urgent every day. During the pandemic some 40pc of agricultural organisations supporting smallholder farmers were forced to close at least temporarily, while more than a third lacked the capital they needed to recover, according to our survey.
The pandemic has exacerbated an already difficult situation for African farmers, with climate change looming as a bigger threat. But when I talk to the young people running African agritech firms, I detect no sense of gloom. These young people exude energy, ideas and optimism. They represent an entire generation that has the potential to transform African agriculture for the better. That gives me hope for the future. In a time filled with hardship, we should embrace their vision and make it our own.
PUBLISHED ON
Aug 28,2021 [ VOL
22 , NO
1113]


Viewpoints | Nov 02,2024

Advertorials | Jun 05,2023

Commentaries | Jul 05,2025

Radar | May 06,2023

Fortune News | Jan 07,2024

Photo Gallery | 180829 Views | May 06,2019

Photo Gallery | 171022 Views | Apr 26,2019

Photo Gallery | 162140 Views | Oct 06,2021

My Opinion | 137331 Views | Aug 14,2021

Dec 22 , 2024 . By TIZITA SHEWAFERAW
Charged with transforming colossal state-owned enterprises into modern and competitiv...

Aug 18 , 2024 . By AKSAH ITALO
Although predictable Yonas Zerihun's job in the ride-hailing service is not immune to...

Jul 28 , 2024 . By TIZITA SHEWAFERAW
Unhabitual, perhaps too many, Samuel Gebreyohannes, 38, used to occasionally enjoy a couple of beers at breakfast. However, he recently swit...

Jul 13 , 2024 . By AKSAH ITALO
Investors who rely on tractors, trucks, and field vehicles for commuting, transporting commodities, and f...
Nov 1 , 2025
The National Bank of Ethiopia (NBE) issued a statement two weeks ago that appeared to...

Oct 25 , 2025
The regulatory machinery is on overdrive. In only two years, no fewer than 35 new pro...

Oct 18 , 2025
The political establishment, notably the ruling party and its top brass, has become p...

Oct 11 , 2025
Ladislas Farago, a roving Associated Press (AP) correspondent, arrived in Ethiopia in...

Nov 2 , 2025
The National Bank of Ethiopia (NBE) has scrapped the credit-growth ceiling that had s...
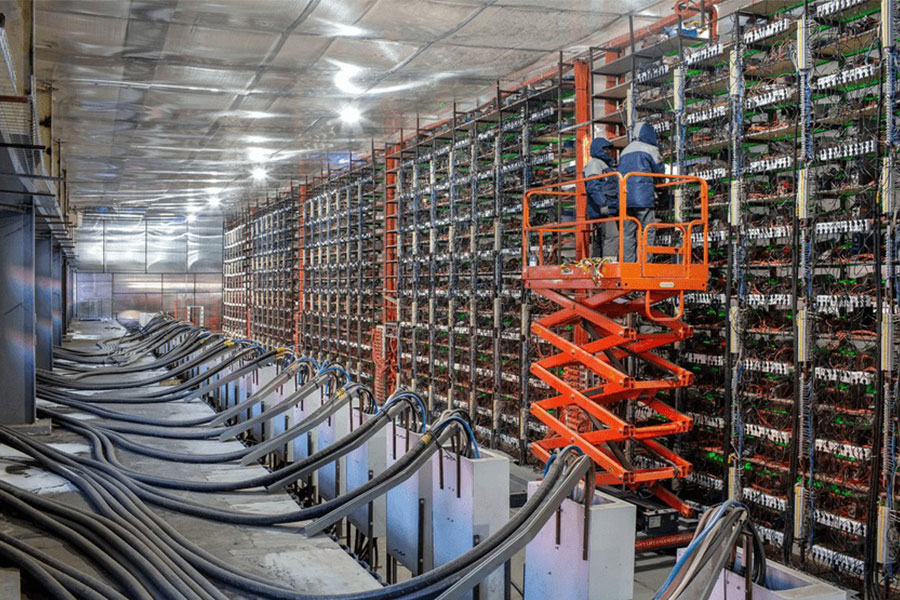

Nov 2 , 2025 . By SURAFEL MULUGETA
The burgeoning data mining industry is struggling with mounting concerns following th...
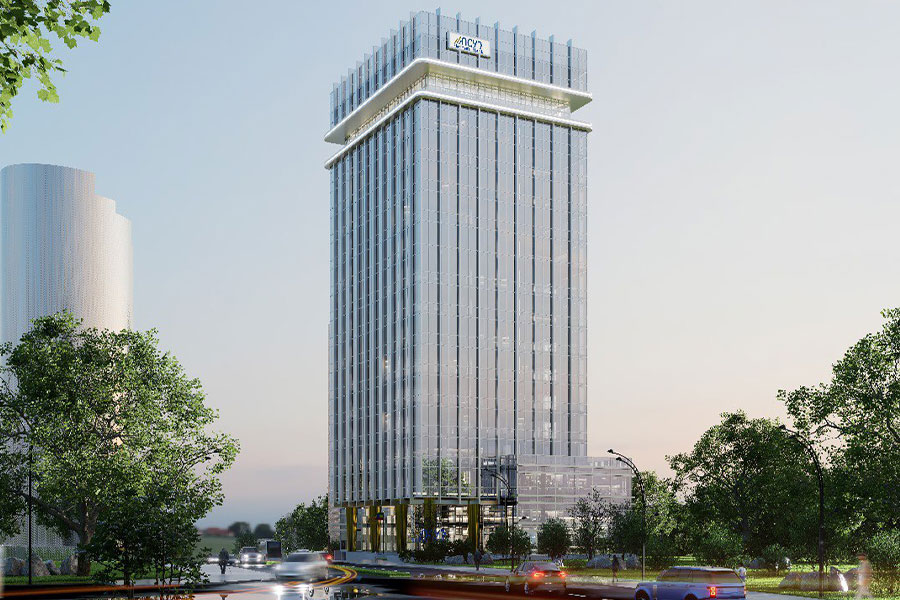

Nov 2 , 2025 . By YITBAREK GETACHEW
Berhan Bank has chosen a different route in its pursuit of a new headquarters, opting for a transitional building instea...

Nov 2 , 2025 . By BEZAWIT HULUAGER
Nib International Bank S.C. has found itself at the epicentre of a severe governance...